nginx学习记录--前端配置nginx实现跨域
前端配置nginx实现跨域
前言:以前做过jsonp实现跨域,不过这种需要服务端配合。现在的前端项目,比如vue,react等,在配置项目的脚手架中就带有跨域设置,也可以自己写一个node服务来跨域,今天来简单学习一下用nginx来实现跨域。
1.什么是nginx
nginx是一个高性能的HTTP和反向代理服务器,也是一个IMAP/POP3/SMTP代理服务器。 nginx的作用是:反向代理,负载均衡。其特点是占有内存少,并发能力强。
2.nginx安装
2-1 windows版:
nginx下载地址:http://nginx.org/en/download.html
nginx官网提供了三个类型的版本:
- Mainline version:Mainline 是 Nginx 目前主力在做的版本,可以说是开发版 .
- Stable version:最新稳定版,生产环境上建议使用的版本
- Legacy versions:遗留的老版本的稳定版
建议使用稳定版。下载之后解压,解压路径中尽量不要有中文,实际上各种环境配置,软件安装等目录尽量都不要用中文,因为中英文字符编码不一样。
解压之后的目录就是这样
windows中常用的操做命令,一下命令全在上面根目录进行,用系统自带命令行,比如cmd。
1.启动nginx。实际上点击nginx.exe也能打开nginx,但是不容易关闭,需要到任务管理器中找到相关服务强行停止掉,建议使用下面命令行开启服务。
start nginx
nginx默认使用80端口,如果电脑中有其他服务占用了80端口,修改nginx使用的端口即可。
server {
listen 80; // 这里改成其他的,比如8082
server_name localhost;
}
2.重启nginx,修改nginx配置之后就需要重启一下
nginx -s reload
3.停止nginx。建议使用后面那种停止方式
nginx -s stop
nginx -s quit
nginx停止命令stop与quit参数的区别在于stop是快速停止nginx,可能并不保存相关信息,quit是完整有序的停止nginx,并保存相关信息。nginx启动与停止命令的效果都可以通过Windows任务管理器中的进程选项卡观察。
4.其他nginx命令(一般很少用到)
-?,-h : 打开帮助信息
-v : 显示版本信息并退出
-V : 显示版本和配置选项信息,然后退出
-t : 检测配置文件是否有语法错误,然后退出
-q : 在检测配置文件期间屏蔽非错误信息
-s signal : 给一个 nginx 主进程发送信号:stop(停止), quit(退出), reopen(重启), reload(重新加载配置文件)
-p prefix : 设置前缀路径(默认是:/usr/local/Cellar/nginx/1.2.6/)
-c filename : 设置配置文件(默认是:/usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf)
-g directives : 设置配置文件外的全局指令
2-2 mac版
1.打开终端,安装Command Line tools ,基本上应该都安装过这个,可以跳过
xcode-select --install
2.安装brew命令
ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
3.安装nginx
brew install nginx
4.启动nginx
sudo nginx
5.mac版nginx命令,基本上和windows差不多
sudo nginx // 启动
sudo -s reload // 重启
sudo -s quit // 停止
sudo -s stop // 停止
6.nginx安装目录
open /usr/local/etc/nginx/
3.nginx配置
nginx启动之后,访问http://localhost:8082/,因为我修改了nginx的默认端口为8082。
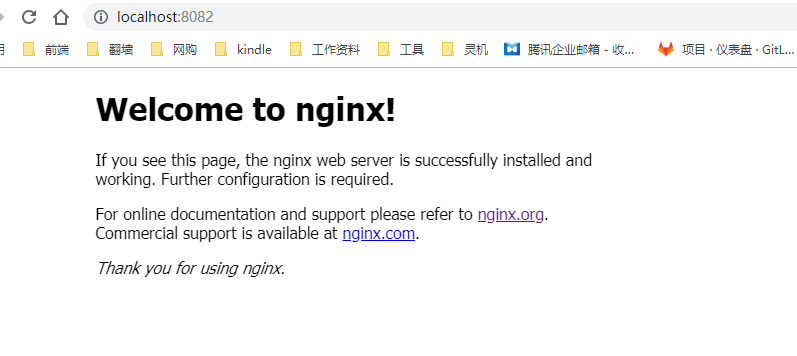
3-1 配置详解
我们先看一下nginx的默认配置,在conf文件夹中,找到nginx.conf文件。在我这路径为E:\nginx-1.14.2\conf\nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
上面文件,简单点说就是
main
events {
....
}
http {
....
upstream myproject {
.....
}
server {
....
location {
....
}
}
server {
....
location {
....
}
}
....
1.main(全局设置) 。主要控制nginx子进程的所属用户/用户组、派生子进程数、错误日志位置/级别、pid位置、子进程优先级、进程对应cpu、进程能够打开的文件描述符数目等。
2.events(nginx工作模式) 。控制nginx处理连接的方式
3.http(http设置) 。是nginx处理http请求的主要配置模块,大多数配置都在这里面进行。
4.sever(主机设置) 。是nginx中主机的配置块,可以配置多个虚拟主机。
5.location(URL匹配) 。是server中对应的目录级别的控制块,可以有多个。
6.upstream(负载均衡服务器设置) 。是nginx做反向代理和负载均衡的配置块,可以有多个。
3-1实战练习
下面我们用豆瓣api V2开放接口来做实验。
接口地址:http://api.douban.com/v2/movie/top250?start=25&count=25
axios请求:
axios.get({
method:'get',
url:"/v2/movie/top250?start=25&count=25"
}).then((res)=>{
console.log(res.data)
})
或者使用jquery
$.get("/v2/movie/top250?start=25&count=25", function(data){
console.log(data);
})
要实现跨域,只需要简单修改几个设置。
1.修改默认配置,大概在35行,80端口改为8082,当然,其他数字也可以,只要是未被占用的端口
listen 80;
2.反向代理到webpack-server服务
默认代理服务为
location / {
root html;
add_header Cache-Control no-store;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' '*';
index index.html index.htm;
}
修改为下面这样,建议注释掉上面部分,新增下面这部分内容。
location / {
# 反向代理到webpack-server服务
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8081;
}
这个匹配规则是,匹配到路由中有/的部分就代理到http://127.0.0.1:8081,相当于全局匹配。。
然后我们在nginx配置文件中,新增一条配置
server {
location ^~ /v2/movie {
proxy_pass http://api.douban.com;
}
}
这里个规则是匹配到 /v2/movie路由之后,重定向到http://api.douban.com
这里需要注意一点,proxy_pass这里,http://api.douban.com和http://api.douban.com/是不一样的。
- 不加
/的情况,访问http://10.1.70.229:8082/v2/movie/v2/movie/top250?start=25&count=25会得到http://api.douban.com/v2/movie/top250?start=25&count=25(符合预期的) - 加/的情况,访问
http://10.1.70.229:8082/v2/movie/v2/movie/top250?start=25&count=25会得到http://api.douban.com/top250?start=25&count=25(不符合预期)
下面两种配置效果是一样的。
location ^~ /v2/movie {
proxy_pass http://api.douban.com;
}
或
location ^~ /v2/movie {
proxy_pass http://api.douban.com/v2/movie/;
}
针对这种情况,如果后端接口统一有了规定前缀,比如/api,那你这里就不要配置斜杠了。另一种情况,后端接口shit一样,没有统一前缀,这边又要区分,那就在前端所有接口都加一个统一前缀,比如/api,然后通过加斜杠来替换掉好了~
删掉多余注释代码,整个nginx.conf文件配置如下。
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 8082;
server_name gwg.localhost;
location / {
# 反向代理到webpack-server服务
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8081;
}
# 匹配豆瓣api
location ^~ /v2/movie {
# rewrite ^/v2/movie/(.*)$ /$1 break;
proxy_pass http://api.douban.com;
}
# 匹配到错误之后的处理页
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
3-3 rewrite
rewrite功能就是,使用nginx提供的全局变量或自己设置的变量,结合正则表达式和标志位实现url重写以及重定向。rewrite只能放在server{},location{},if{}中,并且只能对域名后边的除去传递的参数外的字符串起作用,例如 http://seanlook.com/a/we/index.php?id=1&u=str 只对/a/we/index.php重写。语法rewrite regex replacement [flag];
如果相对域名或参数字符串起作用,可以使用全局变量匹配,也可以使用proxy_pass反向代理。
表明看rewrite和location功能有点像,都能实现跳转,主要区别在于rewrite是在同一域名内更改获取资源的路径,而location是对一类路径做控制访问或反向代理,可以proxy_pass到其他机器。很多情况下rewrite也会写在location里,它们的执行顺序是:
- 执行server块的rewrite指令
- 执行location匹配
- 执行选定的location中的rewrite指令
如果其中某步URI被重写,则重新循环执行1-3,直到找到真实存在的文件;循环超过10次,则返回500 Internal Server Error错误。
还是使用豆瓣的接口
接口地址:http://api.douban.com/v2/movie/top250?start=25&count=25
在js中这样访问,注意多了 /api 部分
$.get("/api/v2/movie/top250?start=25&count=25", function(data){
console.log(data);
})
配置中的location修改为
location ^~ /api/ {
rewrite ^/api/(.*)$ /$1 break;
proxy_pass http://api.douban.com/;
}
这里解释为:匹配到请求路径中包含 /api/部分时候,将/api/这部分替换为http://api.douban.com/
也就是说请求的是http://10.1.70.229:8082/api/v2/movie/top250?start=25&count=25,实际上已经代理到http://api.douban.com/api/v2/movie/top250?start=25&count=25,得到了接口的数据
3-4 location
自出引用自 https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000002797606#articleHeader0
语法规则: location [=|~|~*|^~] /uri/ { … }
= 开头表示精确匹配
^~ 开头表示uri以某个常规字符串开头,理解为匹配 url路径即可。nginx不对url做编码,因此请求为/static/20%/aa,可以被规则^~ /static/ /aa匹配到(注意是空格)。
~ 开头表示区分大小写的正则匹配
~* 开头表示不区分大小写的正则匹配
!~和!~*分别为区分大小写不匹配及不区分大小写不匹配 的正则
/ 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到。
多个location配置的情况下匹配顺序为(参考资料而来,还未实际验证,试试就知道了,不必拘泥,仅供参考):
首先匹配 =,其次匹配^~, 其次是按文件中顺序的正则匹配,最后是交给 / 通用匹配。当有匹配成功时候,停止匹配,按当前匹配规则处理请求。
location = / {
#规则A
}
location = /login {
#规则B
}
location ^~ /static/ {
#规则C
}
location ~ \.(gif|jpg|png|js|css)$ {
#规则D
}
location ~* \.png$ {
#规则E
}
location !~ \.xhtml$ {
#规则F
}
location !~* \.xhtml$ {
#规则G
}
location / {
#规则H
}
那么产生的效果如下:
访问根目录/, 比如http://localhost/ 将匹配规则A
访问 http://localhost/login 将匹配规则B,http://localhost/register 则匹配规则H
访问 http://localhost/static/a.html 将匹配规则C
访问 http://localhost/a.gif, http://localhost/b.jpg 将匹配规则D和规则E,但是规则D顺序优先,规则E不起作用,而 http://localhost/static/c.png 则优先匹配到 规则C
访问 http://localhost/a.PNG 则匹配规则E, 而不会匹配规则D,因为规则E不区分大小写。
访问 http://localhost/a.xhtml 不会匹配规则F和规则G,http://localhost/a.XHTML不会匹配规则G,因为不区分大小写。规则F,规则G属于排除法,符合匹配规则但是不会匹配到,所以想想看实际应用中哪里会用到。
访问 http://localhost/category/id/1111 则最终匹配到规则H,因为以上规则都不匹配,这个时候应该是nginx转发请求给后端应用服务器,比如FastCGI(php),tomcat(jsp),nginx作为方向代理服务器存在。
暂时就了解到这里了,后续有机会再次学习…….