offset、client和scroll三大家族对比
一、关于网页中位置和距离的各种操作
因为最近做的一个需求需要用到上拉刷新,这时候需要判断某个dom对象的位置,这是又想起了曾经折磨过我的三大家族。
网页可见区域宽: document.body.clientWidth;
网页可见区域高: document.body.clientHeight;
网页可见区域宽: document.body.offsetWidth (包括边线的宽);
网页可见区域高: document.body.offsetHeight (包括边线的宽);
网页正文全文宽: document.body.scrollWidth;
网页正文全文高: document.body.scrollHeight;
网页被卷去的高: document.body.scrollTop;
网页被卷去的左: document.body.scrollLeft;
1、offSet家族
offSet 自己的,用于获取元素自己本身的尺寸 。
1-1、offsetHeight和offsetWidth
获取对象自身的宽度和高度 ,包括内容、边框和内边距,即:offsetWidth = width + border + padding
1-2、offsetLeft 和 offsetTop
距离第一个有定位的父级盒子左边和上边的距离,注意:父级盒子必须要有定位,如果没有,则最终以body为准!  总结:offsetLeft和offsetTop从从父标签的padding开始计算,不包括border。即:从子盒子边框到定位父盒子边框的距离。
总结:offsetLeft和offsetTop从从父标签的padding开始计算,不包括border。即:从子盒子边框到定位父盒子边框的距离。
1-3、offsetParent
**返回当前对象的父级(带有定位)盒子,可能是父级元素,也可能是父级元素的父级……
- 如果当前元素的父级元素没有进行CSS定位(position:absolute 或 relative),则其offsetParent为body; 如果当前元素的父级元素中有CSS定位(position:absolute或relative),offsetParent取最近的那个父级元素。
1-4、offsetXXX 和 style.XXX的区别
用offsetLeft和style.left来分析,其他的以此类推:
a) style.left只能获取行内的,而offsetLeft则可以获取到所有的;
b) offsetLeft 可以返回没有定位盒子距离左侧的位置;而style.left不可以,其只能返回有定位盒子的left;
c) offsetLeft 返回的是数字,而 style.left 返回的是字符串,除了数字外还带有单位:px;
注意:可以用parseInt进行转化;比如:styleLeft='300px' ---> parseInt(styleLft) ---> 300
d) offsetLeft是只读的,而style.left是可读写;
e) 如果没有给 当前 元素指定过 top 样式,则 style.top 返回的是空字符串。
2、scroll家族
- 网页正文全文宽: document.body.scrollWidth;
- 网页正文全文高: document.body.scrollHeight;
- 网页被卷去的高: document.body.scrollTop;
- 网页被卷去的左: document.body.scrollLeft;
在实际开发中使用比较多的就是scrollTop,如下图: 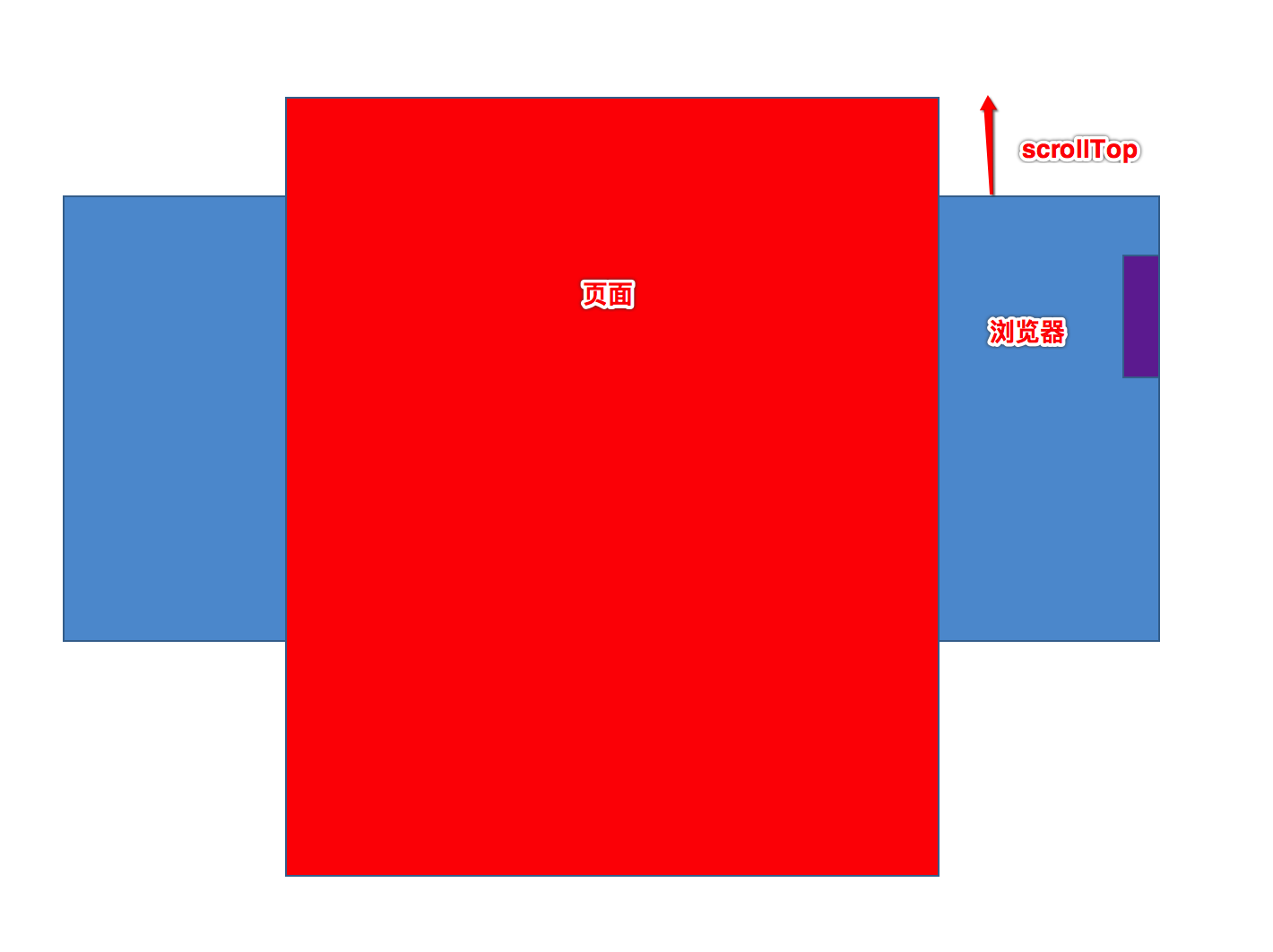
2-1、处理scroll家族浏览器适配问题
- ie9+ 和 最新浏览器
window.pageXOffset; (scrollLeft)
window.pageYOffset; (scrollTop)
Firefox浏览器 和 其他浏览器
document.documentElement.scrollTop;Chrome浏览器 和 没有声明 DTD
document.body.scrollTop;兼容写法
var scrollTop = window.pageYOffset || document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop || 0; var scrollLeft = window.pageXOffset || document.documentElement.scrollLeft || document.body.scrollLeft || 0;
2-1、scrollTo(x,y)
- 把内容滚动到指定的坐标
- 格式:scrollTo(xpos,ypos)
- xpos 必需;要在窗口文档显示区左上角显示的文档的 x 坐标;
- ypos 必需;要在窗口文档显示区左上角显示的文档的 y 坐标 。
- 网页大部分都没有水平滚动条,所以,这个x 不太常用。
3、client家族
3-1、 clientWidth和clientHeight
- 网页可见区域宽: document.body.clientWidth;
- 网页可见区域高: document.body.clientHeight;
3.2、 clientLeft和clientTop
clientLeft,clientTop
- 返回的是元素边框的borderWidth,
- 如果不指定一个边框或者不定位改元素,其值就为0
· Client家族和offset家族一样只能获取不能设置
· clientWidth=width+padding
· clientHeight=height+padding
·
· 不常用:
· clientTop=获取左边框的宽度
· clientLeft=获取上边框的宽度
二、 offset、client和scroll的区别分析
left和top分析:
clientLeft: 左边边框的宽度;clientTop: 上边边框的宽度
clientWidth=width+padding
clirntHeight= height+padding
offsetLeft: 当前元素距离有定位的父盒子左边的距离;offsetTop: 当前元素距离有定位的父盒子上边的距离
offectWidth= width+padding+border
offextHeight= height+padding+border
scrollLeft: 左边滚动的长度; scrollTop: 上边滚动的长度;
scrollWidth=内容的宽度
scrollHeight=内容的高度
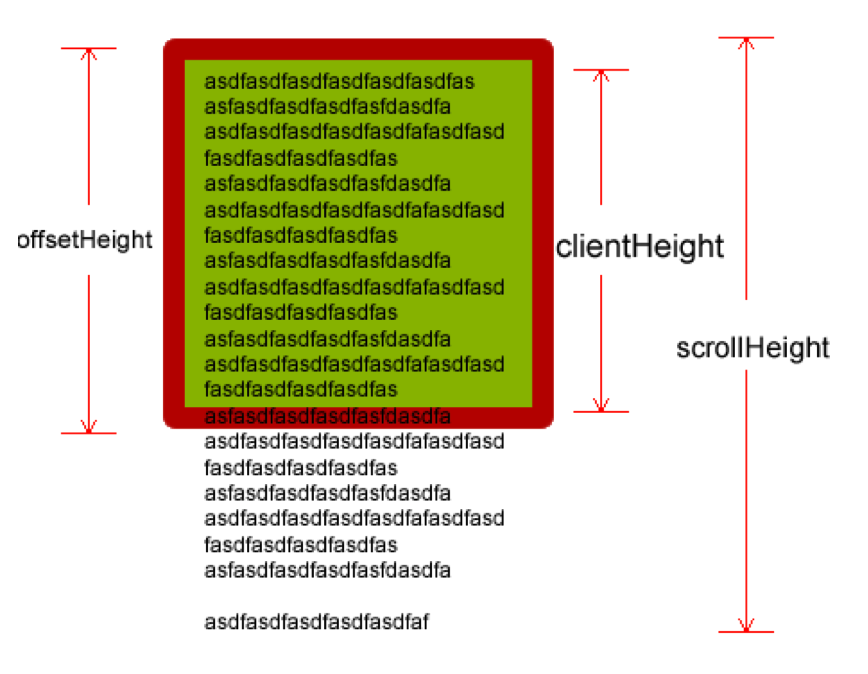
width和height分析
- clientWidth / Height: 内容 + 内边距
- offsetWidth / Height: 内容 + 内边距 + 边框
- scrollWidth / Height: 滚动内容的宽度和高度
三、获取屏幕的可视区域
ie9及其以上的版本、最新浏览器
window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight标准模式浏览器
document.documentElement.clientWidth, document.documentElement.clientHeight怪异模式
document.body.clientWidth, document.body.clientHeight通用写法
function client() { if(window.innerWidth){ // ie9及其以上的版本 return{ width: window.innerWidth, height: window.innerHeight } }else if(document.compatMode != 'CSS1Compat'){ // 怪异模式 return{ width: document.body.clientWidth, height: document.body.clientHeight } } // 标准 return{ width: document.documentElement.clientWidth, height: document.documentElement.clientHeight } }